“GingerMaster” Takes Advantage of Root Exploit against Android 2.3
Google Android malware is on the rise, and now a team of researchers has uncovered the first malicious program to use a root-level exploit against Android 2.3.

In partnership with mobile security vendor NetQin, researchers at North Carolina State University (NC State) have reported finding GingerMaster, which they claim takes advantage of the most recent root exploit against Android platform 2.3 (also known as Gingerbread).
“The GingerMaster malware is repackaged into legitimate apps,” explained Xuxian Jiang, an associate professor at NC State’s computer science department, in a blog post. “These legitimate apps are supposedly popular to attract user downloads and installation. As this is the first time such malware has been identified, it is not surprising when our experiments show that it can successfully evade the detection of all tested (leading) mobile anti-virus software,” he added.
According to NetQin, GingerMaster registers a receiver so that it will be notified when the system finishes booting. Inside the receiver, it will silently launch a service in the background that collects sensitive information such as the device ID and phone number and then uploads the data to a remote server.
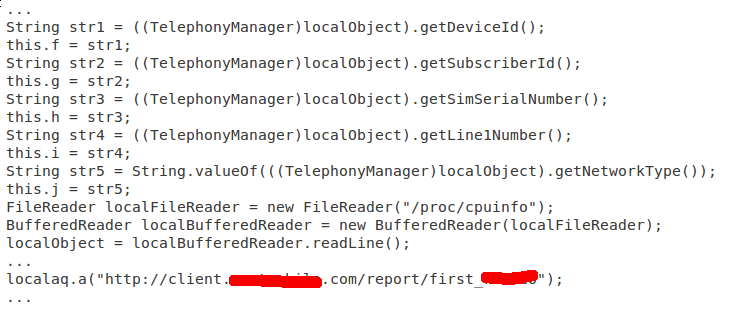
The root exploit is packaged into an infected app via a file called gbfm.png, Jiang blogged. Once the exploit is launched, GingerMaster will attempt to install a root shell with file mode 4755 into a system partition for later use.
“After getting root privilege, [the] GingerMaster malware will connect to the remote C&C server and wait for instructions,” the researcher blogged.
He recommended using “common sense” mobile security practices as a defense, for example only downloading apps from trusted app markets and checking the permissions applications request.
Suggested Reading: Mitigation of Security Vulnerabilities on Android & Other Open Handset Platforms
Suggested Reading: Attacks on Mobile and Embedded Systems: Current Trends
















