Unpatched and unprotected VMware ESXi servers around the world have been targeted over the past few days in a large-scale ransomware attack exploiting a vulnerability patched in 2021.
The attacks, dubbed ESXiArgs, are still being analyzed by the cybersecurity community, but based on the information available to date, it appears that threat actors are exploiting CVE-2021-21974, a high-severity ESXi OpenSLP heap-overflow vulnerability that VMware patched in February 2021.
“A malicious actor residing within the same network segment as ESXi who has access to port 427 may be able to trigger the heap-overflow issue in OpenSLP service resulting in remote code execution,” VMware said in its advisory at the time.
Proof-of-concept (PoC) code and technical details on CVE-2021-21974 were made public a couple of months after the patches were announced, but there do not appear to be any previous reports of the vulnerability being exploited in the wild.
In the ransomware attacks that surged over the weekend, threat actors exploited the flaw to hack ESXi servers and deploy a piece of malware that encrypts files associated with virtual machines, including files with the .vmdk, .vmx, .vmxf, .vmsd, .vmsn, .vswp, .vmss, .nvram, .vmem extensions, according to an analysis by French cloud company OVH.
The attacks seem to target vulnerable ESXi servers that are exposed to the internet on port 427.
OVH noted that the malware shuts down VM processes before initiating its encryption routine, but the function does not seem to work properly. In some cases, files are only partially encrypted, allowing victims to recover them without paying a ransom. There is no evidence of data being stolen in the attacks.
Researcher Enes Sonmez has found a way to recover some of the files encrypted by the ransomware.
The attacks were initially incorrectly attributed to ransomware named Nevada and Cheerscrypt (Emperor Dragonfly), but they were later linked to a new ransomware operation named ESXiArgs.
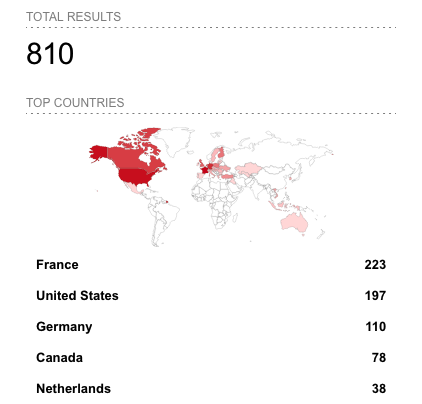
More than two thousand ESXi instances appear to be impacted according to Censys. Shodan shows roughly 800 compromised servers.
At the time of writing, many antivirus engines cannot detect the ESXiArgs malware.
Government agencies in the United States and Europe are looking into these attacks and assessing their impact.
While the malware does not appear to have file exfiltration capabilities, the ransom note dropped in the ESXiArgs attack informs victims that their data will be sold unless a payment is made. Victims are instructed to pay 2 bitcoins ($48,000) to receive the encryption key needed to recover files.
Ransomware expert Soufiane Tahiri has been keeping track of the Bitcoin wallet addresses used by the cybercriminals.
While it has become increasingly common for threat actors to target ESXi servers, the exploitation of ESXi vulnerabilities is rare.
Related: VMware Patches VM Escape Flaw Exploited at Geekpwn Event
Related: VMware Confirms Exploit Code Released for Critical vRealize Logging Vulnerabilities















