Mobile security firm Lookout has been monitoring the evolution of the Android Trojan dubbed “NotCompatible”, and they say the latest version of the malware is sophisticated enough to pose a threat to protected enterprise networks.
NotCompatible.A, which researchers discovered in 2012, acted as a proxy on infected devices, but it didn’t cause any direct damage. The mobile malware’s authors did not use a complex command and control (C&C) architecture and communications were not encrypted, making it easy for security solutions to detect its activities.
New features in NotCompatible.C
The latest version of the threat, NotCompatible.C, is far more complex. According to Lookout, the authors have made it more difficult to detect and resilient to takedowns by implementing features usually found in mature PC-based malware.
 NotCompatible.C uses peer-to-peer (P2P) communications between infected devices, which makes it resilient to IP and DNS blocking, and it relies on multiple C&C servers that are geographically distributed, which enables the malware to function properly even if law enforcement authorities manage to shut down individual servers.
NotCompatible.C uses peer-to-peer (P2P) communications between infected devices, which makes it resilient to IP and DNS blocking, and it relies on multiple C&C servers that are geographically distributed, which enables the malware to function properly even if law enforcement authorities manage to shut down individual servers.
The malware’s authors have also started encrypting all C&C and proxied traffic, making it difficult for network security solutions to identify the malicious traffic. Furthermore, public key cryptography is used for mutual authentication between C&C servers and clients.
In an effort to protect their infrastructure, the cybercriminals use a gateway C&C to analyze incoming connections, and block those that come from IP addresses that are not trusted.
NotCompatible.C distribution and use
NotCompatible.C is distributed through spam campaigns and compromised websites. The attackers are not leveraging any exploits, but instead rely on social engineering to trick potential victims into installing the threat on their mobile devicese. One of the distribution campaigns observed by Lookout used the classic “security update” ruse.
According to the security firm, the cybercriminals have acquired compromised websites and accounts in bulk. In one of the spam runs seen by researchers, only Yahoo accounts had been used. In a different campaign, the attackers used only compromised AOL accounts.
These techniques have been successful. Lookout says its solutions have blocked hundreds of thousands of infection attempts in the United States and other countries around the world. In the U.S. for instance, NotCompatible reached encounter rates of more than 1% at its peak, researchers noted.
Experts believe the malicious actors behind NotCompatible have adopted a rent-a-botnet business model, and are either providing access to their botnet to other cybercriminals, or they are a multi-faceted group. The botnet has been leveraged for spam campaigns (weight loss), for bulk ticket purchasing (Craigslist, Ticketmaster, StubHub), brute-force attacks against WordPress website administration panels, and c99 shell control (logging into shells and performing various actions).
Attacks against protected networks
Lookout says it has not seen NotCompatible.C being used in attacks targeted at corporate networks. However, the company has detected hundreds of networks with devices that have encountered the malware.
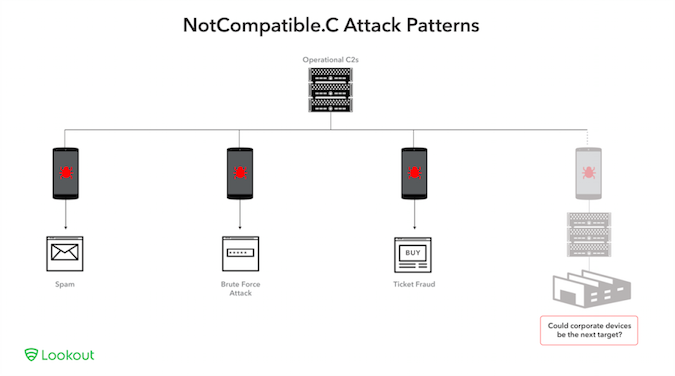
“As soon as a device carrying NotCompatible.C is brought into an organization on a mobile device, it could provide the operators of this botnet with access to the organization’s network. Using the NotCompatible proxy, an attacker could potentially do anything from enumerating vulnerable hosts inside the network, to exploiting vulnerabilities and search for exposed data,” Lookout researchers explained in a blog post.
NotCompatible is a great tool for targeting corporate networks because it’s difficult to detect and block by network-based security systems. Its traffic is encrypted to avoid raising any red flags, and P2P communications enable the malware to function even if organizations block known C&C servers at network layer, Lookout said.
“As a mobile botnet with widespread distribution and proxy capabilities, the potential use of NotCompatible.C as a gateway to attack protected networks and systems is not only plausible, but a likely outcome,” experts warned.












