Facebook announced today that the source code of its capture the flag (CTF) platform has been made available on GitHub.
The social media giant says its goal is to help those who want to learn about hacking and allow them to put their skills to the test. The company wants to make security education more accessible to schools, students and non-profit organizations. The platform has been released under a Creative Commons license for use by non-commercial entities for educational purposes.
Facebook’s CTF platform includes everything one needs to run a hacking competition, including a game map, team registration and a scoring system. Some challenges can also be provided upon request, including for reverse engineering, web application security, forensics, binary exploitation, and cryptography. Users can also utilize the Facebook CTF platform to build custom challenges.
There are two types of challenges: trivia questions on computer security, and flag problems that involve exploits and hacks. Flag challenges require participants to complete a task such as dumping a database, getting a shell on the system, or manipulating an application.
“Not only do CTFs have the ability to teach more technical skills than you’ll get in an average computer science program, they can also help you break into the security industry,” said Gulshan Singh, a software engineer on Facebook’s threat infrastructure team. “When I started looking for full-time positions, I found security job interviews to be a lot like CTF challenges, which made it easier for me to demonstrate my technical skills — and I was able to make an impact from day one.”
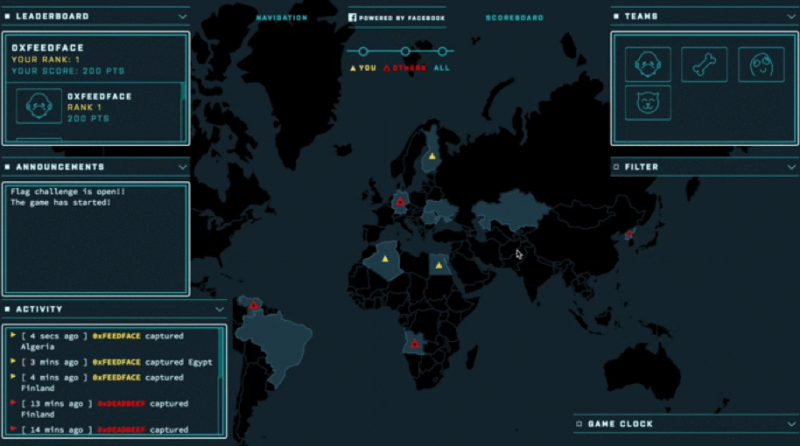
The platform can be set up on a system running Ubuntu (on a physical or virtual machine). Facebook has provided instructions on how to install and use its CTF platform.
The company noted that the CTF is also included in its bug bounty program so vulnerabilities found in the platform itself should be disclosed via that channel.
It’s not uncommon for major tech companies to open source in-house developed tools. Last year, Netflix released an XSS flaw discovery framework called Sleepy Puppy and, in March, Google released its Vendor Security Assessment Questionnaire (VSAQ) framework.
Related Reading: Attackers Increasingly Abuse Open Source Security Tools
Related Reading: Password Cracking Tool Hashcat Goes Open Source










