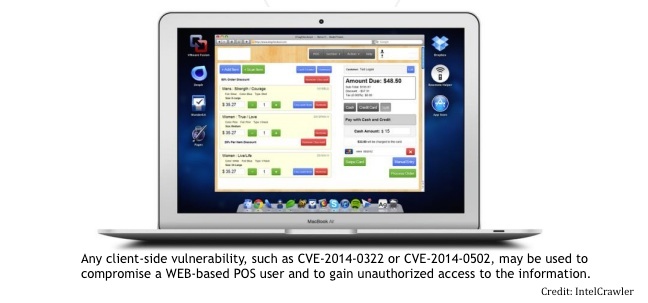
Attackers are targeting vulnerabilities in major Web browsers to compromise cloud-based point-of-sale (PoS) systems, according to cyber threat intelligence firm, IntelCrawler.
The malware, called POSCLOUD by IntelCrawler, targets cloud-based PoS software commonly used by grocery stores, retailers, and other small businesses, the company wrote in a report released Wednesday.
Unlike most PoS malware, POSCLOUD doesn’t bother with RAM scraping to intercept payment card information before the system gets a chance to encrypt the data. Instead, the malware relies on keylogging and stealth screenshots to steal personal information and financial data, which are then sold on underground forums to identity thieves, IntelCrawler said.
Researchers initially uncovered the malware after a big botnet takedown, said Andrew Komarov, CEO of IntelCrawler.
Many of these cloud systems integrate with locally-attached hardware such as credit card readers, barcode scanners, cash drawers, and receipt printer and process payments in the cloud. Merchants can also store credit card details for customers to use in future transactions and personal identifiable information to use in loyalty campaigns within the application.
The fact that POSCLOUD has keylogging capabilities means attackers can still access the encrypted data, IntelCrawler said. Attackers just use the intercepted passphrase to access the application to log in and view all the data, decrypted. The malware also connects with a command-and-control server to download additional malware, which can intercept form data and login credentials, as well as check for network connections to specific PoS service providers, IntelCrawler said.
Researchers observed two main attack vectors. Application operators and supervisors may be tricked in a targeted attack to visit a malicious site, which launches a drive-by download attack, Komarov said. Attackers also send spoofed messages pretending to be from the cloud-based PoS service provider containing malicious attachments, he said.
POSCLOUD is also different from earlier PoS malware such as BlackPOS or Dexter because it doesn’t matter what operating system the system has. This malware attacks cloud applications through the Web browser, so regardless of what browser the merchant is using—whether it’s Internet Explorer, Apple’s Safari, or Google Chrome—the merchant is at risk.
POSCLOUD exploits two flaws, the double free vulnerability in Adobe Flash Player (CVE-2014-0502) and the user-after-free vulnerability in Internet Explorer (CVE-2014-0322), IntelCrawler said. The Flash Player flaw was part of a targeted attack earlier in the year which infected several non-profit organizations’ websites. The IE bug was used in the attack against the Veterans of Foreign Wars website in February.
While cloud-based technologies give retailers—especially smaller merchants—access to essential systems and advanced features for an affordable price, it’s clear there is a security gap. Considering Microsoft and Adobe have already patched both vulnerabilities, merchants have to do a better job updating the computers they use to access the cloud-based systems.
IntelCrawler notified multiple PoS service providers about the attacks and provided law enforcement officials with the list of infected IP addresses, many of appear to be in the U.S. and E.U. The company expects to see an increase in these types of attacks.
The full report from IntelCrawler is available online in PDF format.













