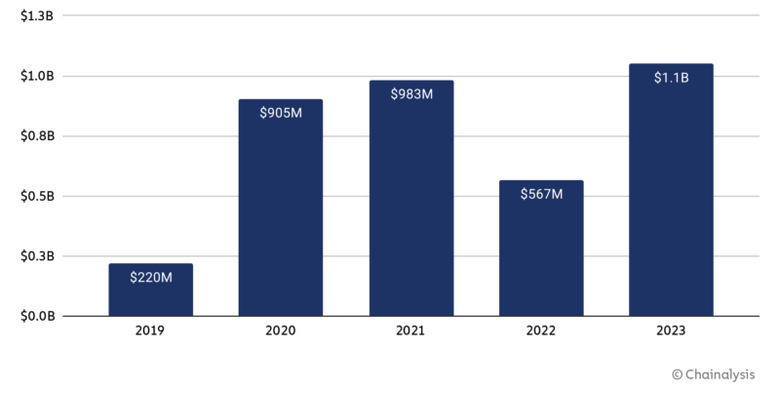
The payments made by victims of ransomware attacks doubled in 2023 compared to the previous year, exceeding $1 billion, according to blockchain analysis firm Chainalysis.
The company has looked at the cryptocurrency wallets known to be used by cybercrime groups to receive ransom payments from victims and found a total of $1.1 billion, up from $557 million in 2022.
It’s worth noting that these amounts are “conservative estimates” and they may increase as new cryptocurrency wallet addresses are identified. For instance, when it published its 2022 report, Chainalysis only identified $457 million in ransom payments, but that number has since gone up by $100 million. The number for 2021 increased from $766 million to $983 million over the past year.
It’s also worth pointing out that these figures only represent the actual ransom payments, not other damages suffered by companies hit by ransomware.
Chainalysis highlighted in its report for 2022 that ransomware payments had dropped, attributing it to the increasing use of data backups, cyberinsurance policy changes, and fear of sanction violations.
Now the company says 2022 was an anomaly, not a trend, and 2023 was a record high.
“In 2023, the ransomware landscape saw a major escalation in the frequency, scope, and volume of attacks,” Chainalysis said.
The number of threat actors involved in ransomware attacks increased in 2023, with threat intelligence firm Recorded Future seeing 538 new ransomware variants. In addition, cybercriminals are making more money due to increasingly focusing on big game hunting, which involves targeting high-value organizations from which they can demand bigger ransom payments.
Ransomware-as-a-service, where affiliates get many of the resources they need from the ransomware operators, has been making it increasingly easy to carry out attacks. In addition, initial access brokers (IABs) have also made it easier for cybercriminals to conduct data theft and file-encryption attacks.
“We found a correlation between inflows to IAB wallets and an upsurge in ransomware payments, suggesting monitoring IABs could provide early warning signs and allow for potential intervention and mitigation of attacks,” Chainalysis said.
As for how the cybercriminals launder ransomware payments, the company found that centralized cryptocurrency exchanges and mixers appear to be the preferred methods for many groups.
“However, this year saw the embrace of new services for laundering, including bridges, instant exchangers, and gambling services. We assess that this is a result of takedowns disrupting preferred laundering methods for ransomware, some services’ implementation of more robust AML/KYC policies, and also as an indication of new ransomware actors’ unique laundering preferences,” Chainalysis noted.
Related: $1.7 Billion Stolen in Cryptocurrency Hacks in 2023: Analysis
Related: North Korean Hackers Have Stolen Over $3 Billion in Cryptocurrency: Report


















