A new study by NSS Labs places Internet Explorer 9 (IE9) at the top of the heap when it comes to blocking socially-engineered malware attacks.
With its SmartScreen Filter and Application Reputation technologies enabled, IE9 was able to block 99.2 percent of live threats globally during a test conducted between May 27 and June 10. The test stacked IE up against Google Chrome 12, Apple Safari 5, Mozilla Firefox 4 and Opera 11, and included a list of roughly 1,200 malicious URLs.
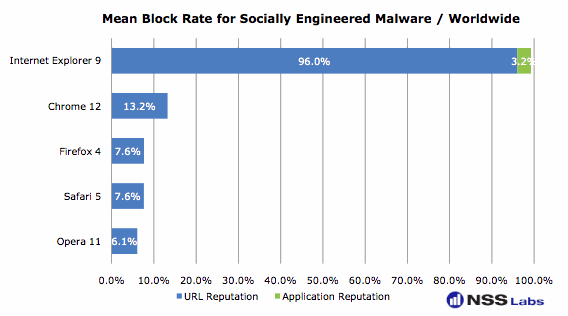
Despite the fact that all five browsers make use of a reputation system, the other four did not fare nearly as well as IE – Google Chrome caught only 13.2 percent of the malicious URLs, while Safari and Firefox each blocked 7.6 percent. Opera scored the lowest, blocking 6.1 percent, according to the study.
“The significance of Microsoft’s new application reputation technology cannot be overstated,” the report states. “Application reputation is the first attempt by any vendor to create a definitive list of every application on the Internet. This new capability helps users discern malware, and potentially unsafe software from actual good software. The list is dynamically created and maintained, much the same way Google, (or Bing) is continuously building and maintaining a library of content for search purposes.”
NSS also ranked the browsers according to how fast each added newly discovered malicious URLs to their block lists. IE9 again led the way, stopping more than 99 percent of the URLs at the gate within the first hour when its Application Reputation technology was enabled. Safari by comparison stopped just 6.4 percent during the first 60 minutes.
NSS Labs used the following definition to describe a socially-engineered malware URL: “A web page link that directly leads to a download that delivers a malicious payload whose content type would lead to execution, or more generally a website known to host malware links.” The full report is available here.
















