Researchers at Websense uncovered an effort by spammers to target mobile devices using what are known as quick response codes for URLs.
Quick response (QR) codes are a type of matrix barcode that are often used by mobile devices to bring people to a particular URL. The codes can be read by any mobile device with a camera and a QR reader.
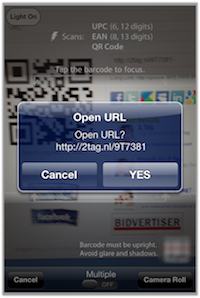 According to Websense, the emails typically try to push pharmaceutical products, and include a link to the Website 2tag.nl – a legitimate Web service that allows users to create QR codes for URLs.
According to Websense, the emails typically try to push pharmaceutical products, and include a link to the Website 2tag.nl – a legitimate Web service that allows users to create QR codes for URLs.
Once the 2tag.nl URL is loaded in the browser, a QR code and the Website it resolves to will appear. When the QR code is read by a QR reader, it automatically loads the spam URL (in some cases it may ask before loading depending on the QR reader installed). The end result is improved click-through rates for spammed sites.
“This is the first time we have seen a QR code used in an active spam campaign,” Patrik Runald, senior manager of security research at Websense, told SecurityWeek. “Because QR codes are the ultimate URL obfuscator, with the right social lure, QR codes can become increasingly more successful in driving users to websites hosting malware targeting the mobile device. Although, at this point, we believe the bad guys are just trying to gauge their relative success through spam, and are just getting their bearings.”
In October, Kaspersky Lab noted that its research team had detected the first attempts by cyber-criminals to use QR codes in malicious attacks. The company found several malicious Websites containing QR codes for mobile apps on the Android platform that included a Trojan capable of sending text messages to premium-rate short numbers.
By early October, Kaspersky Lab researchers had detected QR codes linked to malware for both Android and J2ME.
“We expect malicious QR codes to grow in number, especially as QR codes become more mainstream,” according to the company. “Currently the safest way to protect yourself is to be cautious of scanning QR codes and avoid anything that looks suspicious.”
Runald said users should also make sure their QR reader applications displays the destination URL and provides an option for stopping automatic direction to Websites. Users can also protect themselves by using an e-mail security or Web security gateway to prevent the likelihood of infection.












