Triada Trojan Exists in RAM and Uses Zygote Process to Hook All Applications on Android
Security researchers at Kaspersky Lab recently came across a new Trojan targeting Android devices, which they say is the most advanced mobile malware seen to date.
Dubbed Triada (Backdoor.AndroidOS.Triada), this malware family was mainly designed to redirect financial SMS transactions to buy additional content or steal money from the user. What sets the Trojan apart, however, is a modular architecture combined with the ability to infiltrate all process on the infected system to achieve high persistence.
The malware’s modular architecture allows operators to do almost anything on the device, being limited only by the capabilities of the operating system itself, the researchers say.
As Kaspersky Lab’s Nikita Buchka and Mikhail Kuzin explain in a blog post, the malware is distributed via an “advertising botnet” that included malware families such as Leech, Ztorg, and Gorpo, along with a new malware family Trojan.AndroidOS.Iop. Armed with rooting capabilities, these Trojans distribute each other on the infected devices, and also download and install other applications.
The Triada Trojan stands out in the crowd because it can use the Zygote parent process to implement its code in the context of all software on the device. The Zygote process contains system libraries and frameworks that almost all apps use and is a template for each new app, meaning that the Trojan runs in each application, since it enters the process and is part of the template.
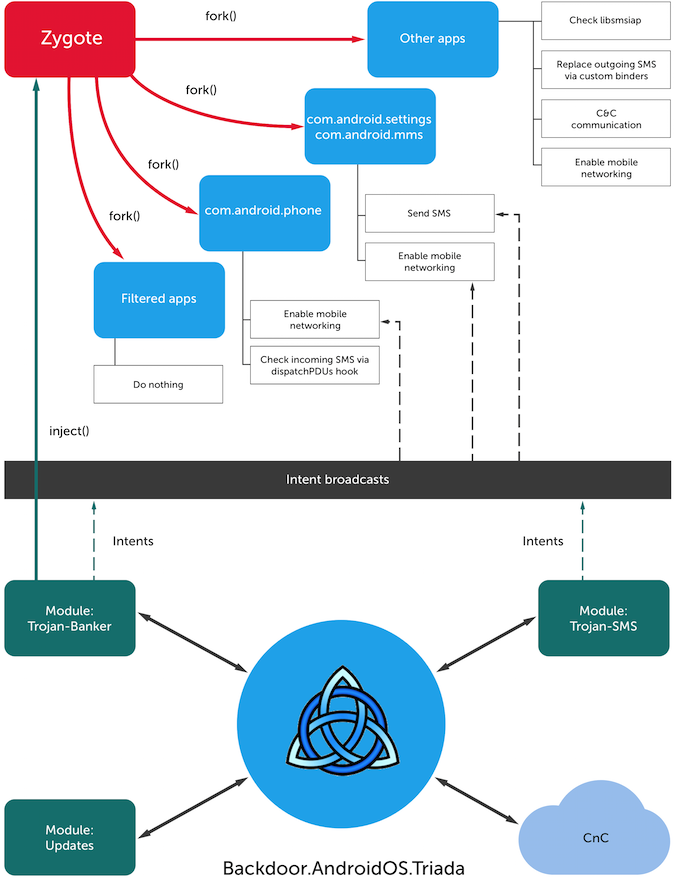
Because Triada actively uses root privileges to substitute system files and exists mostly in the mobile device’s RAM, it extremely difficult to detect, Kaspersky says.
The Trojan manages to hide its modules from the list of running services, as well as from the list of running applications, from the list of installed packages, and from the list of installed applications.
The techniques used by the Trojan haven’t been found in any other known mobile malware and Kaspersky Lab researchers say that this is the most advanced and dangerous malicious application targeting the mobile OS.
According to Kaspersky, given that the malware penetrates all applications installed on the system, its operators can potentially modify their logic to implement new attack vectors.
Full details with more technical information are available in from Kaspersky Lab.
Related: Source Code of Android Banking Trojan “GM Bot” Leaked
Related: Xbot Android Trojan Steals Banking Info, Encrypts Devices












