Researchers at Dutch security firm Securify have conducted a detailed analysis of the Android banking Trojan known as Marcher and discovered that a single botnet has managed to steal a significant number of payment cards.
Marcher has been around since late 2013, but it initially attempted to trick users into handing over their payment card details using Google Play phishing pages. In March 2014, the malware started targeting banks in Germany and, by the summer of 2016, there had already been more than 60 targeted organizations in the U.S., U.K., Australia, France, Poland, Turkey, Spain and other countries.
The malware has been disguised as various popular apps, including Netflix, WhatsApp and Super Mario Run.
Securify has identified nine Marcher botnets over the last 6 months, and each of them has been provided with new modules and targeted web injects by the Trojan’s creators.
One of these botnets, which mainly targets the customers of banks in Germany, Austria and France, has infected more than 11,000 devices, including 5.700 in Germany and 2,200 in France. The attackers’ C&C server stored 1,300 payment card numbers and other banking information.
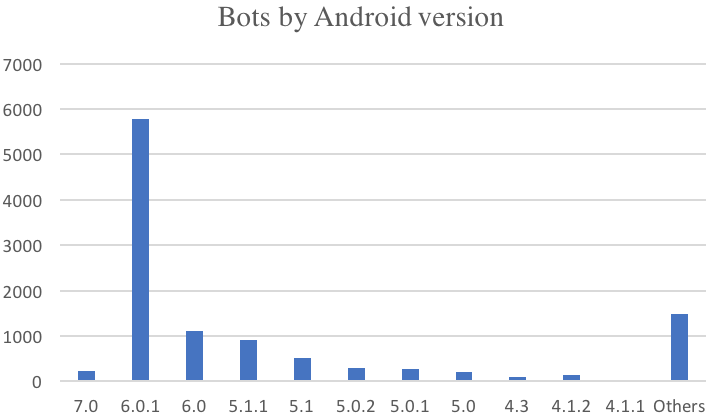
Based on the analysis of the command and control (C&C) server used by the cybercriminals, researchers determined that a majority of the infected devices had been running Android 6.0.1, but the list of victims also included more than 100 Android 7.0 devices.
Marcher monitors the applications launched by the victim, and when one of the targeted apps is detected, an overlay screen is displayed in an effort to trick the user into handing over sensitive information.
“Marcher is one of the few Android banking Trojans to use the AndroidProcesses library, which enables the application to obtain the name of the Android package that is currently running in the foreground. This library is used because it uses the only (publicly known) way to retrieve this information on Android 6 (using the process OOM score read from the /proc directory),” Securify researchers explained.
In order to avoid being removed by security products, Marcher blocks popular mobile antivirus applications. Seven months ago, researchers said the Trojan had been blocking eight antiviruses, but Securify’s report shows that the malware currently targets nearly two dozen products.
“Based on the statistics we found on this one C2 panel we researched and the amount of different C2 panels out there, we believe that the potential financial losses due to Android banking Trojans are, or will soon be, bigger than the current losses from desktop malware like Gozi and Dridex, especially since hardly any of the banking apps seem to detect the attack,” experts said.
Related: Hundreds of Thousands of Android Trojans Installed from Unknown Sources Daily
Related: “Switcher” Android Trojan Hacks Routers, Hijacks Traffic
Related: Source Code for BankBot Android Trojan Leaks Online















