UK-based cybercrime disruption services provider Netcraft has spotted thousands of phishing pages placed by cybercriminals in special directories that are present on millions of websites.
In the past month, the company spotted more than 400 new phishing websites hosted in a folder named /.well-known/. This directory serves as a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) path prefix that allows users and automated processes to obtain policy and other information about the host.
The /.well-known/ directory is commonly used to demonstrate ownership of a domain. The administrators of HTTPS-protected websites that use Automatic Certificate Management Environment (ACME) to manage SSL certificates place a unique token inside the /.well-known/acme-challenge/ or /.well-known/pki-validation/ folders to show the certificate issuer that they control the domain.
“Consequently, most of the phishing attacks that make use of the /.well-known/ directory have been deployed on sites that support HTTPS, using certificates issued by ACME-driven certificate authorities like Let’s Encrypt and cPanel,” Netcraft’s Paul Mutton explained.
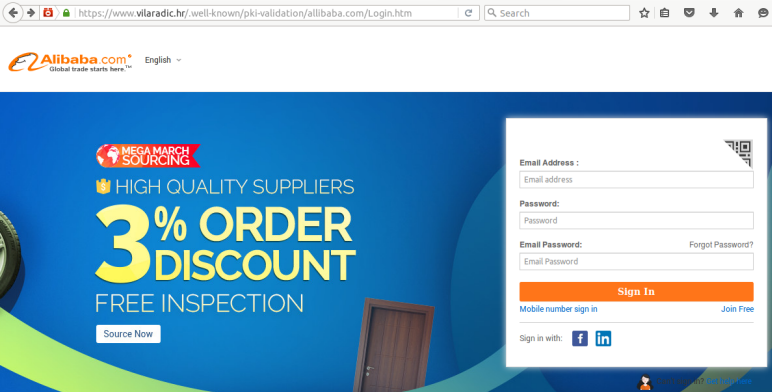
The /.well-known/ location can be a great place to hide a phishing page due to the fact that while the folder is present on millions of websites – mainly due to the success of ACME and Let’s Encrypt – many administrators are not aware of its presence.
Mutton noted that since there is a dot in front of the directory’s name, listing files using the ls command will not display it as files and folders that start with “.” are hidden. In an effort to make their phishing pages even more difficult to find, cybercriminals have placed them in subdirectories of /acme-challenge/ and /pki-validation/.
“Shared hosting platforms are particularly vulnerable to misuse if the file system permissions on the /.well-known/ directories are overly permissive, allowing one website to place content on another customer’s website,” Mutton warned. “Some of the individual servers involved in these attacks were hosting ‘well-known’ phishing sites for multiple hostnames, which lends weight to this hypothesis.”
The expert pointed out that while /acme-challenge/ and /pki-validation/ are not the only well-known URIs, these are the only ones that have been used to host phishing sites.
Netcraft said it was not clear how malicious actors had hijacked the websites found to be hosting these phishing pages.
Related: Number of Phishing Sites Using HTTPS Soars
Related: Stanford University Site Hosted Phishing Pages for Months















