NortonLifeLock this week released the beta version of a free browser extension that allows Twitter users to easily identify bots on the social media platform.
The tool, named BotSight, is currently available for Chrome, Chromium-based Brave, and Firefox for users in the US, UK, Australia and New Zealand. Its developers also plan on creating a smartphone app and a version that works with Microsoft Edge.
BotSight was created by the NortonLifeLock Research Group, formerly known as Symantec Research Labs — the NortonLifeLock brand was created after Symantec sold its enterprise security unit and Symantec brand to Broadcom for $10.7 billion.
NortonLifeLock says BotSight, which it describes as a research prototype, uses a machine learning model to detect Twitter bots with a high degree of accuracy, including in tweets displayed in the user’s timeline, search and trending topics. It analyzes more than 20 features to determine if a Twitter account is a bot, including the account name and description, and its follower increase rate.
When users install the BotSight extension, they will see a percentage and a green, yellow or red icon next to the name of each profile, including ones mentioned in a tweet. This icon indicates the likelihood of an account being a human or bot.
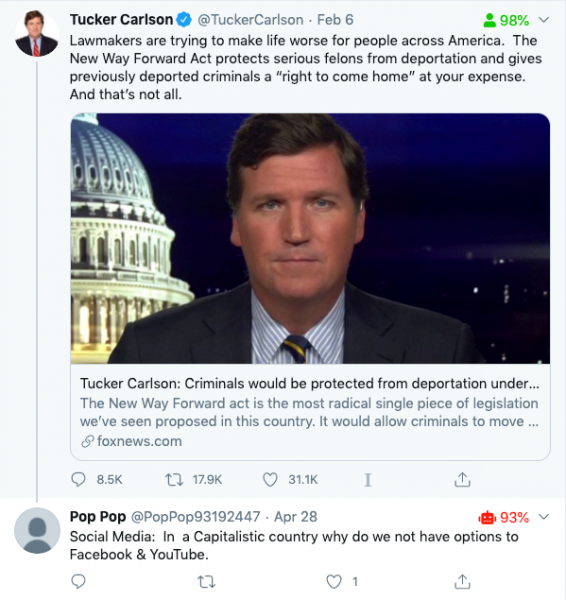
The company has so far analyzed more than 100,000 accounts and found that roughly 5% of tweets are posted by bots.
“In our analysis of recent coronavirus-related tweets, we found that between 6-18% of users tweeting on this subject were bots, depending on which time period we sampled, while a random sample of the Twitter stream indicates 4-8% bot activity by volume over the same time period. This contrast shows that bots are strategic about their behaviour: favoring current events to maximize their impact,” said Daniel Kats, principal researcher at the NortonLifeLock Research Group.
NortonLifeLock this week reported a $614 million revenue for the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020, slightly lower than the $617 million reported one year ago.
Related: Twitter Unveils New Processes for Fighting Spam, Bots
Related: Botnet of 3 Million Twitter Accounts Remains Undetected for Years
Related: Researchers Find Thousands of Twitter Amplification Bots in Just One Day















