A team of researchers from Google has identified a new Rowhammer attack technique that works against recent generations of dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) chips.
Rowhammer attacks — first discussed in 2014 — involve repeatedly accessing a row of memory in an effort to cause bit flips in adjacent rows, which can be useful for bypassing memory protections. A malicious actor could use Rowhammer to escalate privileges and for other purposes, and researchers have demonstrated over the past years that attacks can be launched remotely and against mobile devices.
JEDEC, an organization that develops open standards and publications for the microelectronics industry, has warned that Rowhammer attacks can pose a “serious threat to cloud service providers, data centers, laptops, smart phones, self-driving cars and IoT devices.”
The vulnerability exists because the memory cells in DRAM chips have been placed very close together to increase capacity and decrease size. This makes it more difficult to prevent cells from electrically interacting with each other.
Rowhammer defenses in many cases assume that the attacker can only cause bit flips in the immediate neighbors of the row they are targeting. However, the new attack method disclosed this week by Google, which researchers have dubbed “Half-Double,” shows that the effects of Rowhammer can extend beyond immediate neighbors, thus bypassing some of the existing defenses.
“Given three consecutive rows A, B, and C, we were able to attack C by directing a very large number of accesses to A, along with just a handful (~dozens) to B. Based on our experiments, accesses to B have a non-linear gating effect, in which they appear to ‘transport’ the Rowhammer effect of A onto C,” the Google researchers explained.
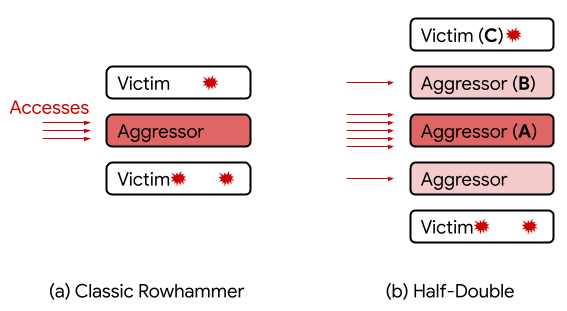
The researchers said the Half-Double attack works against newer generation DRAM chips, but it does not work against older ones, which suggests that the shrinkage of memory cell geometries makes Rowhammer attacks “stronger and longer-ranged.” They also noted that it may be possible to launch attacks that work over distances greater than two rows.
Google has been working with JEDEC and others to come up with mitigations for Rowhammer attacks. JEDEC in March released information on system level and near-term DRAM level mitigations.
“We are disclosing this work because we believe that it significantly advances the understanding of the Rowhammer phenomenon, and that it will help both researchers and industry partners to work together, to develop lasting solutions. The challenge is substantial and the ramifications are industry-wide,” Google researchers said.
Related: Researchers Propose Software Mitigations for Rowhammer Attacks














