Municipal planners in Europe are embracing digital technologies to deliver various services to the citizens. Smart-city services connect Internet-enabled sensors on buses, in rental bike racks, or parking meters, and then make use of an app or SMS with the citizen’s smartphone for payment. But Europe’s rich hacking culture has makers and breakers poking and prodding at these new systems every day. Many can figure out how to hack the services using simple techniques like replay to get free services or, in some cases, make a little bit of money.
Here’s an extreme example.
A city in the Benelux area has a pay-to-park system that prints out a parking receipt that users then display in their car window or dashboard. Hackers have created an app that clones parking receipts. It auto-detects the user’s location to show a list of nearby parking machines and then delivers an image of a valid parking receipt.
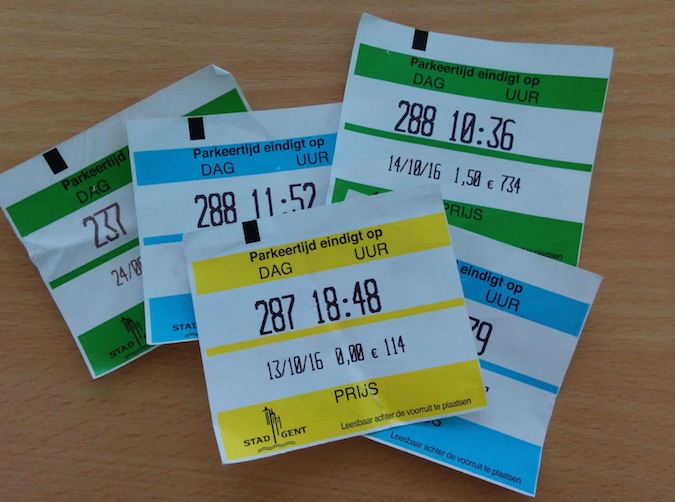
This might sound like a lot of trouble to go through for free parking, but then students (and other young “maker” types) always have more time than money.
“At home you could make tickets to park your car in front of your home or you could make some tickets for where you are going. Or perhaps you’re hosting a party and feel like handing out free parking tickets to your guests. And some use a WiFi printer to print tickets in their car so all they had to do it cut them to size.” —a young hacker familiar with the app
Another Benelux city uses an SMS-based system to distribute one-hour tickets for the public transportation system. Unlike the parking receipts, the SMS tickets have a unique identifier, so they can’t actually be cloned. But hackers there made a web app that allows them to share tickets; one user pays for the first ticket, and if he only uses the transport for 20 minutes, there’s still 40 minutes left. That 40 minutes can be distributed to anyone else using the app. At the end of the month, each app subscriber receives a bill from the app (payable in Bitcoin, of course) for their distributed tickets. In a way, it’s a neat little system to claw back unused travel costs.
Another low-value hack involves the redemption of recyclable bottles at a grocery store. When a consumer finishes a case of beer or soft drinks, he can return the case and scan the barcode to receive a cash redemption. Different types of returnable bottles have different cash redemptions. Smart-city hackers have figured out that the system doesn’t correlate the returned type with the barcode. By making a copy of a higher-value bar code, the city hacker can return a lower-value item but receive the higher-value redemption. Now, surely this discrepancy is so small (mere pennies per transaction) that a city planner wouldn’t (or shouldn’t) build a smarter system to detect the discrepancy; after all, recycling is still happening, which is good. But some citizens are getting better compensation—although maybe after the cost of their printer ink, it’s a wash.
In talking with Europeans, there are two perspectives on these citizen hacker activities. “It’s simple fraud,” said one man at a SecureLink conference in Belgium. A man opposite him disagreed: “It’s just gaming a system, and a citizen is within his right to take advantage where he can.”
The generation of city planners building the new smart cities need to remember this: humans are good at gaming any system. Actually, not good; they’re great. Give a group of people a set of rules, and they will quickly figure out how to beat the system. See blood-doping at the Olympics, or money laundering, or smart-city hacking.
Smart city planners will likely tolerate a small amount of citizen fraud and concentrate real security for higher-value asset systems like electrical grids, traffic lights, and industrial control systems.
Related Reading: IoT Worm Could Hack All Smart Lights in a City














