Google paid out a total of $12 million through its bug bounty programs in 2022. This includes a $605,000 payout that represents the company’s highest reward ever.
More than 700 researchers from 68 countries were rewarded in 2022 for helping Google make its products and services more secure, roughly the same as in 2021. However, the total bug bounties paid out in 2022 were significantly higher than the $8.7 million paid out the previous year.
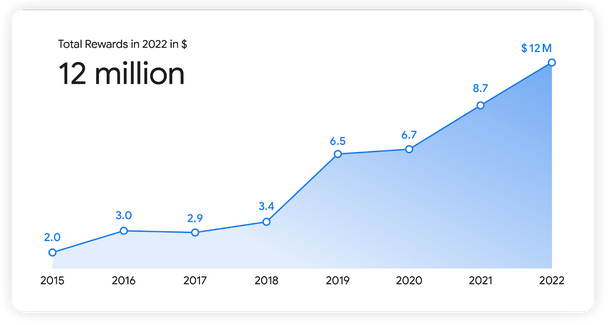
Google said it fixed more than 2,900 issues last year across its products. The $605,000 reward was paid out through the Android Vulnerability Reward Program (VRP), through which the tech giant awarded a total of $4.8 million in 2022.
It’s unclear what the $600k reward was paid for, but Google has been offering up to $1 million for remote code execution vulnerabilities affecting the Pixel Titan M secure chip. In addition, last year it temporarily offered a maximum of $750,000 for data exfiltration flaws in Titan M.
Of the total amount, $486,000 went to the private Android Chipset Security Reward Program (ACSRP), which is run by Google and Android chipset manufacturers. More than 700 vulnerability reports were submitted through this program.
As for the Chrome VRP, Google paid out a total of $4 million, including $3.5 million for 360 vulnerabilities in the Chrome browser and $500,000 for 110 bugs in ChromeOS.
Google has announced that in 2023 it plans on experimenting with the Chrome VRP and informed bounty hunters that it will be offering bonuses.
The company’s Vulnerability Research Grant program continued in 2022, with more than $250,000 in grants awarded to 170 researchers.
Bug bounty hunters rewarded by Google donated more than $230,000 to charities.
Related: Researcher Says Google Paid $100k Bug Bounty for Smart Speaker Vulnerabilities
Related: Google Launches Bug Bounty Program for Open Source Projects
Related: Google Boosts Bug Bounty Rewards for Linux Kernel Vulnerabilities














