Google has taken further steps to protect Internet users against malicious websites by expanding its Safe Browsing efforts in Chrome and search.
The Safe Browsing service is designed to warn users when they are about to access a suspicious website or download malicious software. Now, Chrome users will also be alerted before they visit deceptive sites that encourage them to download unwanted software, the company said in a blog post.
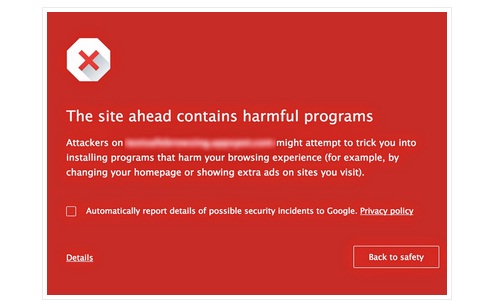
Google has put significant effort into designing security warnings. When Chrome 37 was launched, the company introduced a new SSL warning that improved adherence rates by nearly 30%, Google researchers revealed in a recent study.
As far as search improvements are concerned, the company has integrated signals that identify deceptive websites in order to reduce the chances of users visiting them via search results.
Google has also started disabling ads that point to websites serving unwanted software. It’s not uncommon for cybercrooks to leverage ads in an effort to lure users to their shady websites and one of their favorite tactics is malicious advertising (malvertising). A malvertising campaign first spotted in December abused Google AdSense to redirect users to bogus sites.
Google advises owners to register their websites with Google Webmaster Tools, which alerts them in case anything suspicious is identified on their sites.
Last month, the search giant released the beta version of the Google Cloud Security Scanner, a tool designed to help Google App Engine developers identify cross-site scripting (XSS) and mixed content vulnerabilities.
The tool can prove handy for developers because it’s easy to set up and use, and it’s capable of scanning rich, JavaScript-heavy Web applications.
















