
Study Reveals Big Data Gap: Less Than 1% of World’s Data is Analyzed and Less Than 20% is Protected
In the latest “digital universe” study, analyst firm IDC found that the amount of data being generated is exploding.
In 2020, the total amount of world’s data will be 40 zettabytes, IDC said in its latest Digital Universe report, sponsored by storage giant EMC. In the previous report, released in June 2011, IDC had estimated 35 zettabytes by 2020. The new figure reflects a 50-fold growth from 2010.
How much is 40 zettabytes? It might be easier to think of it as 5,247 GB of data for every person on Earth, according to EMC.
 The report estimated 2.8 zettabytes of data have been created and replicated in 2012. All data is expected to double every two years through 2020, but most of it will be generated by machines talking to each other over networks, according to the report.
The report estimated 2.8 zettabytes of data have been created and replicated in 2012. All data is expected to double every two years through 2020, but most of it will be generated by machines talking to each other over networks, according to the report.
The popularity of computers and mobile devices worldwide, as well increased access to the Internet has contributed to the growth of the digital universe, IDC said. The digital universe, as defined in this report, includes corporate data such as data being read by a card reader, security footage, smart meters, and laboratory experiments, as well as consumer data such as images and videos uploaded to YouTube and other sites, movies shown on HDTVs, and transponders at highway toll booths.
The United States leads the pack as the main producer of data, accounting for about 32 percent, followed by Western Europe at 19 percent. While China currently produces 13 percent of data, by 2020, the country will be generating 22 percent, IDC estimated. Emerging markets are expected to be the main producer by 2020, generating 62 percent of data.
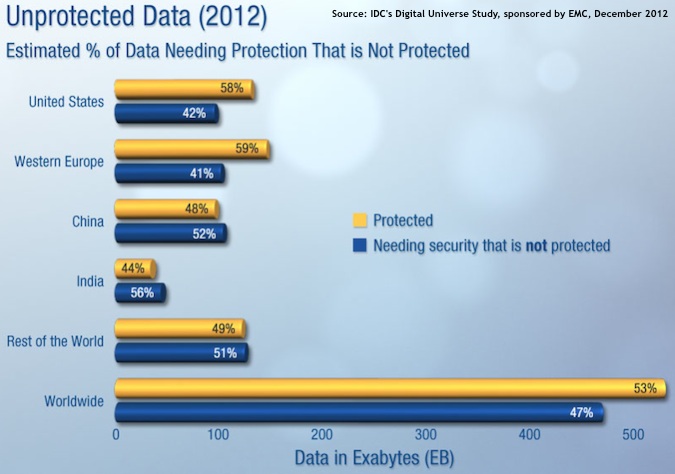
The rapid data growth is outpacing efforts to protect data from theft, prevent snooping, and adhere to regulations. In 2012, about one third of the data in the digital universe needs to be protected, but only 20 percent was actually protected. IDC estimates that 40 percent of data in 2020 will need some form of protection. The level of protection also varies by region, with data in the emerging markets having less protection than the developed markets.
The lack of protection in emerging markets is a major issue because “the geography of the digital universe” is not fixed. Data created in one area easily can wind up in a different geographic region because the user uploaded it to a cloud service, or because the data was replicated to a particular server. If that piece of data had malicious bits or exposes privacy information, than the fact that the originating region didn’t protect the data becomes an issue for other areas.
“The digital universe is like a digital commons, with all countries sharing some responsibility for it,” IDC said.
IDC defined five levels of security that can be used to protect sensitive data: Privacy, Compliance-driven, Custodial, Confidential, and Lockdown. Privacy is the lowest tier of sensitive data, such as the actual email address of the user who uploaded a video to YouTube. Compliance-driven refers to data, such as email messages, that may be subject to eDiscovery and data retention rules. Custodial refers to personal information which could be used to steal a victim’s identity, such as account information. Confidential refers to information the owner wants to protect, such as trade secrets and customer lists. Lockdown is for data requiring the highest security, such as financial transactions, personnel files, medical records, and military intelligence, according to the report.
Of the 40 percent of data that needs to be protected in 2020, IDC estimated about 15 percent will be privacy-related, 5 percent for compliance, 10 percent for custodial, and 5 percent each for confidential and lockdown data.
The study measures all the digital data created, replicated and consumed in the world. There is a gap between the amount of data that could potentially be valuable, and the amount of data actually being used, Tom Corn, chief security officer of RSA, told SecurityWeek. In 2012, 23 percent of the digital universe, or 643 exabytes, was considered useful for business intelligence and other strategic decision-making if tagged and analyzed. However, only 3 percent of the potentially useful data is currently being tagged, Corn said.
By 2020, a third of all the data collected, or 13,000 exabytes, will contain information that may be valuable if analyzed, which is a tremendous opportunity for Big Data analytics, Corn said.
Big data analytics could reveal patterns in social media use, find correlations in scientific studies, overlay medical data over socio-economic information, as well as be used in security forensics. Much of the unstructured data is being lost because no one knows what is buried in all that information. Data, once tagged with metadata, such as a timestamp or geographic location, suddenly becomes more valuable.
Big Data will play a bigger role in information security over the next few years, Corn said. The fact that there is a lack of standards among various sites, increasing number of attacks, and customers disclosing too much information “place considerable private information at risk,” according to the IDC report. What one retailer may consider private, such as transaction and profile data, may not be considered as such by another. Disparate sets of data can be combined to expose private data.
A file containing only Social Security numbers isn’t really that sensitive on its own, Corn noted. It’s when that file is matched up with names or other pieces of data that the list suddenly becomes sensitive and needs to be protected, he said.
Web sites that save, collect, and gather private information have to standardize what they can or cannot do so that individuals’ private information is kept safe, IDC said.
This year’s study marks the first time IDC was able to capture where the information in the digital universe either originated or was first captured or consumed.
EMC has published an interesting interactive version of the report that is available here.













