SQL Slammer, a tiny worm that managed to wreak havoc across the Internet on January 25, 2003, appears to have recommenced activity, Check Point security researchers warn.
The computer worm was first spotted on the day it caused a denial of service condition on tens of thousands of servers worldwide by overloading Internet objects such as servers and routers with a massive number of network packets. Within 10 minutes of its first emergence, SQL Slammer had managed to infect most of its roughly 75,000 victims.
SQL Slammer was based on proof-of-concept code demonstrated at the Black Hat Briefings by David Litchfield, who discovered a buffer overflow bug in Microsoft’s flagship SQL Server and Desktop Engine database products. Although the vulnerability had been patched by Microsoft six months before the worm hit, many installations weren’t patched, and the malicious code could easily propagate.
Also referred to as the Sapphire Worm and Helkern, SQL Slammer is only 376 bytes in size, thus fitting inside a single packet, a feature that allowed it enjoy rapid propagation when it hit. The worm was sending a formatted request to UDP port 1434 and was causing infected routers to start sending the malicious code to random IP addresses, which resulted in a denial of service condition on targets.
Although it remained dormant for over a decade, SQL Slammer appears to have restarted activity, Check Point security researchers warn. According to data collected by Check Point, there was a massive increase in the number of attack attempts between November 28 and December 4, 2016. SQL Slammer was one of the top malware detected in the timeframe.
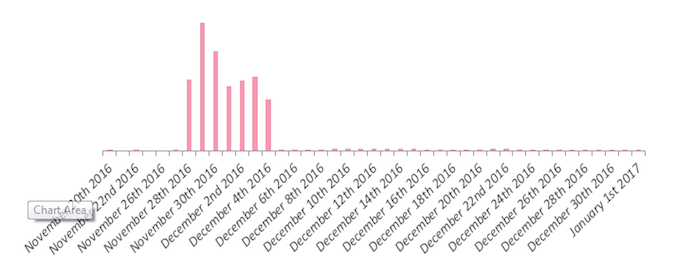
(Image Credit: Check Point)
The number of destination countries of the observed attack attempts was of 172 countries, with 26% of the attacks targeting networks in the United States. According to Check Point, this data shows that the newly recorded SQL Slammer activity wasn’t a targeted attack, but rather a larger wave of attacks.
The security firm also notes that the largest number of attack attempts came from IP addresses located in China, Vietnam, Mexico, and Ukraine.
“To summarize, although the Slammer worm was primarily spread during 2003, and has barely been observed in the wild over the last decade, the massive spike in propagation attempts that was observed in our data leads us to wonder – is the worm trying to make a comeback?” Check Point concludes.
Related: Mirai-Based Worm Targets Devices via New Attack Vector
Related: IoT Worm “Hajime” Uses BitTorrent Protocols for Communications
















