A newly observed piece of ransomware isn’t targeting files to encrypt as most threats in this category do, but rather scrapes Skype and social media profiles for personal information to encourage victims to pay the ransom.
Dubbed Ransoc, the malware connects to social network accounts found on the infected computer, including LinkedIn, Facebook, Skype, and others. Next, the malware searches for torrent files and other content that could point to illegal activity and then displays a ransom note tailored to the findings.
The Ransoc malware, security researchers say, is targeting Windows computers, but it is related to a browser locker that functions cross-platform. The browser locker was spotted in the United States in late October, being distributed through malvertising traffic and targeting Internet Explorer on Windows and Safari on OS X.
While analyzing the threat, Proofpoint security researchers discovered that the threat performs an IP check and sends all traffic through the Tor network. Moreover, they noticed that the malware displays a Penalty Notice only if potential evidence of child pornography or media files downloaded via torrents is found on the infected machine.
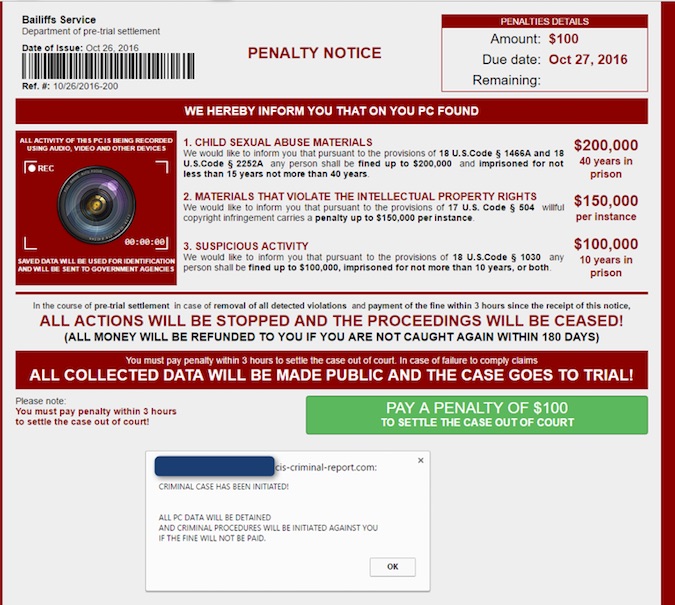
Because it connects to the victim’s social network accounts, the malware customizes the ransom message with accurate data, including profile photos. Victims are threatened that the collected “evidence” would be exposed to the public, and the legitimate social profile information serves as social engineering lure to trick users into believing that sensitive information might actually be at risk.
Ransoc’s code also revealed the ability to access webcams connected to the infected machine, but the security researchers say that the function wasn’t seen active. By threatening the victims with fake legal proceedings if they didn’t pay the ransom, the malware was clearly focused more on people’s reputation than on their files.
The displayed ransom message is a full-screen window that functions like a browser locker application, and which prevents the user from accessing their operating systems or closing the browser window. Additionally, Ransoc checks every 100ms for regedit, msconfig, and taskmgr, and kills their processes, thus preventing the victim from disabling it.
Fortunately, Proofpoint discovered that Ransoc only uses a registry autorun key for persistency. As a result, user can remove the infection by rebooting the computer in Safe Mode. Ransoc’s developer also took a bold approach by using credit card payments for the ransom, which are unusual in when it comes to ransomware, because they could allow law enforcement to trace activity back to the cybercriminal more easily.
“This fairly bold approach to ransom payments suggests the threat actors are quite confident that people paying the ransom have enough to hide that they will probably not seek support from law enforcement. In fact, while Ransoc may seem to be motivated by vigilantism against genuine criminals, the motives are likely less-than-altruistic, as the attackers target users who will be unlikely to resist or inform the authorities and thus increase the likelihood of payment,” Proofpoint says.
This theory is also sustained by the fact that this piece of malware is distributed via malvertising on adult websites and because the penalty notice is displayed only if Ransoc encounters potential evidence of illegally downloaded media and certain types of pornography. The ransom note also claims that money will be sent back if the victim is not caught again in the 180 days.
Related: CryPy Ransomware Uses Unique Key for Each File
Related: DXXD Ransomware Encrypts Files on Unmapped Network Shares
















