Google has patched several vulnerabilities in Caja that could have been exploited for cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks on the Google Docs and Developers domains.
Poland-based bug bounty hunter Michał Bentkowski started analyzing Google Docs at the beginning of the year. The expert noticed that users can create scripts in Google Docs using the JavaScript-based scripting language Google Apps Script.
Google Apps Script uses the search giant’s Caja tool to safely embed HTML, CSS and JavaScript in a website. Caja ensures that user-supplied code is sandboxed to prevent phishing and XSS attacks.
Before executing user code, Caja identifies variables and either replaces them with a Caja-supplied object or removes them from the global scope. This prevents, for instance, the use of the window object for XSS attacks.
Bentkowski discovered that while Caja developers have taken into account that attackers could try to bypass this protection by using obfuscation methods – such as writing window as Function(“win”+”dow”) – they neglected Unicode escapes. The researcher found that window can be written as u0077indow, where the “w” character is replaced with its Unicode representation, u0077.
An attacker could have used this trick to create a specially crafted Google Docs document that included an XSS payload.
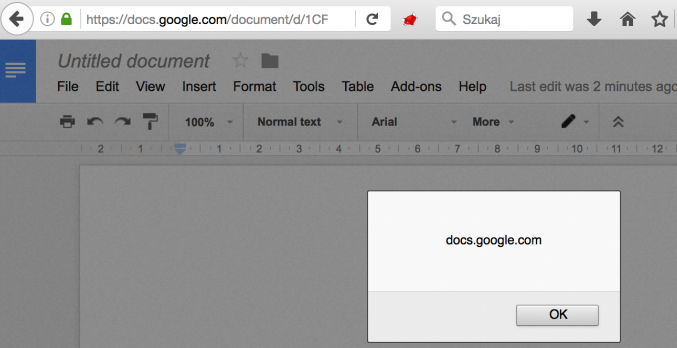
Google addressed this issue after two weeks, but the researcher determined that the fix was not efficient. An attacker could have also replaced the “w” character in window with u{77}. While this method was not as straightforward as the first one, Bentkowski made it work by using HTML-like comments.
Google later patched this vulnerability as well, but the company forgot to update the version of Caja used for demos on the developers.google.com domain. This oversight could have allowed attackers to launch XSS attacks on developers.google.com in combination with web browser clickjacking vulnerabilities.
Caja developers have made some security improvements based on Bentkowski findings. The researcher said Google awarded him $5,000 for the flaws affecting Google Docs and $3,133.7 for the issue on the developer.google.com domain.
Related: Google Increases Android Bug Bounty Payouts
Related: Google Patches Serious Account Recovery Vulnerabilities














