A vulnerability in the Spring Social core library can be exploited by malicious actors to hack users’ accounts on vulnerable websites through a CSRF-style attack.
Developed by Pivotal Software, Spring Social is an extension of the Spring Framework designed to allow developers to connect their Spring applications via Java bindings to APIs from service providers such as Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter and GitHub. Spring Social is leveraged by many projects, including BroadleafCommerce, a popular open-source e-commerce framework written in Java on top of Spring.
Researchers at SourceClear (SRC:CLR), a San Francisco-based security firm that specializes in securing open source code, have analyzed a serious flaw in Spring Social that can be exploited to hijack user accounts. SourceClear, which came out of stealth mode on October 27, identified the root cause of the issue that was first discovered by Kris Bosch of Include Security.
According to researchers, the vulnerability, identified as CVE-2015-5258, exists in the Social Spring authentication feature and it can be exploited via a specially crafted URL to link an attacker’s account on a service like GitHub or Facebook, which SourceClear calls a “social account,” with a victim’s account on a vulnerable website.
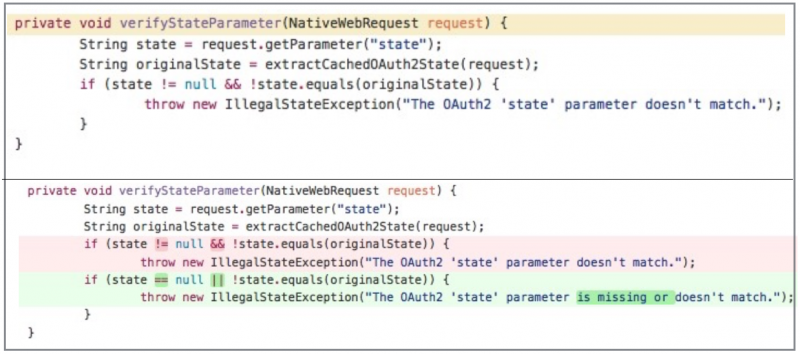
The flaw is related to the OAuth2 authentication process that takes place when a user attempts to connect their account on a vulnerable site to a social account. The issue involves the “state” parameter, which is used for protection against cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks.
At the beginning of an OAuth2 connection flow, a value is assigned to the “originalState” parameter and this value should match the one of the “state” parameter that is sent back from the authentication provider.
Spring Social is designed to check if the value of “state” is not NULL and the values of “state” and “originalState” match. If this condition is not met, an “IllegalStateException” is thrown. The problem is that the validation is not done properly, allowing an attacker to bypass the CSRF protection by stripping the “state” parameter from the request.
Using a specially crafted URL that can be sent to the victim directly or disguised as an image, an attacker can bypass the CSRF protection and connect their own social account with the victim’s account on the vulnerable website. Once this connection is made, the attacker can easily log in to the victim’s account via the social login.
Pivotal Software patched the vulnerability on Thursday with a Spring Social Core update. The flaw has been addressed by adding an additional check for the “state” parameter.