PayPal has addressed a vulnerability that could have been exploited by hackers to insert malicious images into payment pages.
Security researcher Aditya K Sood discovered that the URL of payment pages set up by PayPal users included a parameter called “image_url.” The value of this parameter could have been replaced with a URL pointing to an image hosted on a remote server.
This could have allowed an attacker to use a third-party vendor’s PayPal payment page to deliver malicious images. Sood demonstrated the existence of the flaw by displaying an arbitrary image on a vendor’s payment page, but he believes an attacker could have delivered a piece of malware or an exploit hidden in an image.
Cybercriminals have been known to use harmless-looking image files to hide malware. Such techniques have been used by the developers of the Lurk downloader, the Neverquest malware, the Stegoloader infostealer, and a Brazilian Trojan analyzed recently by Kaspersky.
“This is an insecure design as PayPal allows remote users to inject images owned by them into the PayPal components used for transactions by the customers,” Sood told SecurityWeek. “That being said, the question is — can you deliver malware or an exploit through images? The answer is yes. Exploit techniques such as Stegosploit can be used to achieve that.”
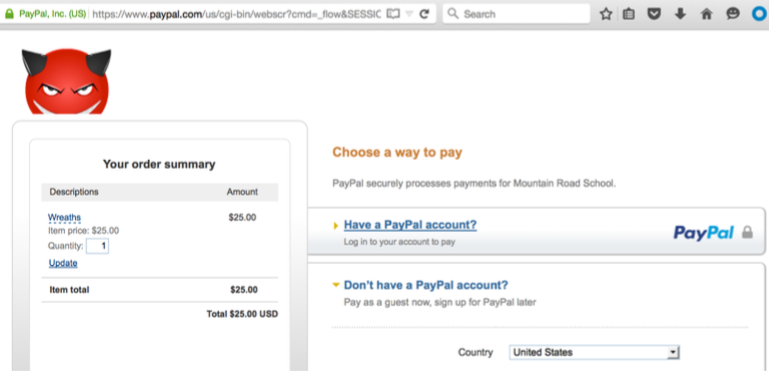
An attacker could have exploited this vulnerability by getting an unauthenticated user to click on a specially crafted link. The fact that the URL was hosted on paypal.com increased the likelihood of the victim opening the link.
The vulnerability was reported to PayPal in January, but it was patched only this month. The company initially said the report did not qualify for a bounty, but it later decided to fix the flaw and award Sood $1,000 for his findings.
The researcher believes this is a high risk issue and he is displeased that the company disagrees with his assessment. PayPal told the expert that the attack scenario he described is unlikely considering that there are much easier ways to deliver malware. The payment processor also noted that it’s actively scanning for malicious content.
Related: Flaw Allowed Hackers to Abuse PayPal Confirmation Emails
Related: PayPal Patches Serious Flaw in Payment System
Related: Deserialization Bug in PayPal App Allowed Code Execution














